API essentials
API routes for Provider-to-SIX API
The connectivity to the debiX API can be established via multiple network channels. The bank can choose which one to rely on for the test and production environments.
Here is a list of the available connectivity channels and related paths:
SSFN
| Environment | URL |
|---|---|
| PROD | https://api.six.ssfn.ch/api/debix-auth/provider-auth/v2 |
| TEST | https://api-preprod.np.six.ssfn.ch/api/debix-auth/provider-auth/v2 |
P2P
| Environment | URL |
|---|---|
| PROD | https://api.p2p.six-group.com/api/debix-auth/provider-auth/v2 |
| TEST | https://api-preprod.np.p2p.six-group.com/api/debix-auth/provider-auth/v2 |
Internet
| Environment | URL |
|---|---|
| PROD | https://api.six-group.com/api/debix-auth/provider-auth/v2 |
| TEST | https://api-preprod.np.six-group.com/api/debix-auth/provider-auth/v2 |
Example
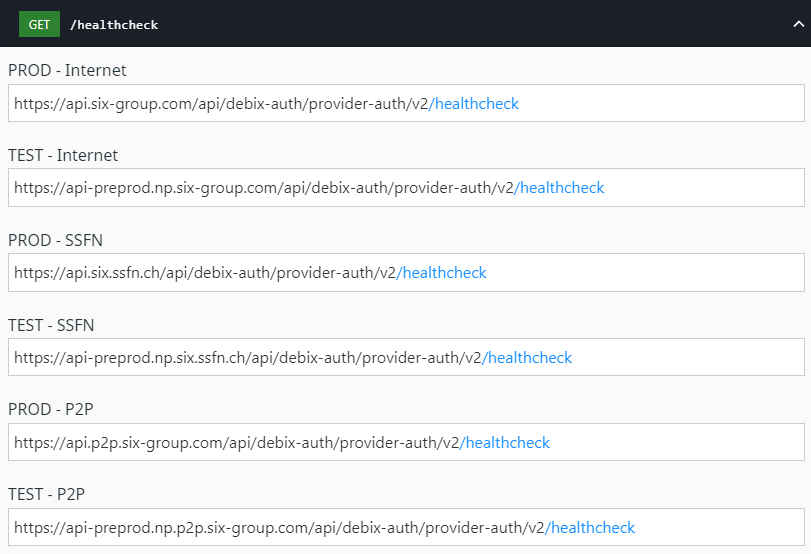
Each path must be combined with the API platform URL. Therefore, all endpoints are defined with a related path.
Here is an example for the /healthcheck endpoint:
Encoding
As defined in RFC4627, the encoding for JSON content is UTF-8.
HTTP verbs
The endpoints use the appropriate HTTP verb for the operations.
| Verb | Description |
|---|---|
GET | Retrieve resources |
POST | Create resources |
PUT | Update resources with full data |
DELETE | Delete resources |
HTTP headers
HTTP headers let the client and the server forward additional information with an HTTP request or response. An HTTP header consists of its case-insensitive name followed by a colon (:), then by its value.
Request headers
The following headers must be used for every request:
accept: application/jsonx-request-idA unique identifier for a request and response pair.content-length: <length>Must be specified for requests with a payload.
Response headers
The API always indicates the return type with a content-type header.
Response codes
The result of the endpoint's operation is reflected in the HTTP status code. The standard HTTP status codes are used:
| HTTP status code | Summary | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 200 | OK | The request was handled successfully |
| 201 | Created | A new resource was created |
| 304 | Not modified | The resource has not been changed |
| 400 | Bad request | The request parameters are invalid |
| 401 | Unauthorized | The authentication information is missing |
| 403 | Forbidden | No access to the resource |
| 404 | Not found | The resource could not be found |
| 500 | Internal server error | An unexpected condition was encountered |
| 503 | Service unavailable | The server cannot handle the request |
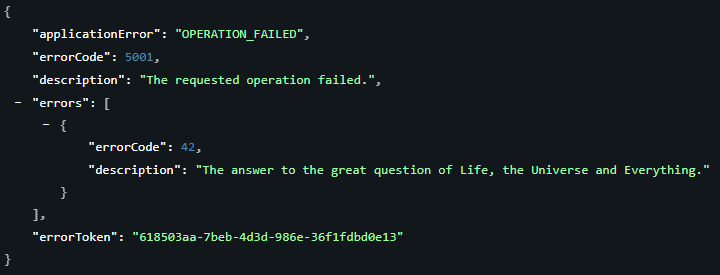
Error responses
Error responses include an HTTP status code and a JSON response body that contains details about the error:
Error codes
The application error codes are used in the body of an error response.
| Application error | Error code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MISSING_MANDATORY_PARAMETER | 4101 | A mandatory parameter is missing. |
| BAD_REQUEST_FORMAT | 4102 | Malformed JSON request. |
| INVALID_PARAMETER_VALUE | 4103 | The validation of the provided request parameters failed. |
| AUTHENTICATION_NOT_PRESENT | 4401 | Authentication request not found. |
| ILLEGAL_STATE | 4402 | Authentication request already processed. |
| OPERATION_FAILED | 5001 | The requested operation failed. |
| TECHNICAL_ERROR | 5002 | An unexpected error occurred. |
Standard error codes
Some application error codes may be returned from any endpoint and are excluded from the detailed endpoint descriptions:
- 4401
- 5001
- 5002
Request validation error codes may be returned from any POST and PUT endpoint with request arguments and are excluded from the detailed endpoint descriptions:
- 4102
- 4103